
Blockchain: a Beginner’s Guide to Understanding This Revolutionary Technology
Welcome to the exciting world of blockchain! If you’ve ever wondered what this revolutionary technology…
The European Blockchain Services Infrastructure (EBSI) represents a pioneering initiative by the European Union, aimed at harnessing the transformative power of blockchain technology to facilitate cross-border services and enhance administrative operations. Launched in 2018 under the aegis of the European Blockchain Partnership (EBP), a collaboration involving all EU Member States, the EBSI is designed as a foundational digital architecture to support a secure, transparent, and efficient delivery of public services across the European Union.
The EBSI’s inception is rooted in the collective recognition of blockchain’s potential to streamline administrative processes, ensure data integrity, and foster trust among participants. By leveraging a network of distributed nodes across member states, the EBSI endeavors to implement interoperable blockchain solutions that address common challenges within the EU, such as the verification of educational credentials, the authenticity of documents, and the facilitation of reliable digital identities.
EBSI aims to build the European blockchain infrastructure by establishing nodes running blockchain-based services. It focuses on creating a network of distributed blockchain nodes to ensure secure and efficient data management.
One of the primary goals of EBSI is to provide verifiable credentials for users across Europe, enhancing trust and authenticity in various sectors, including the public sector.
By leveraging blockchain technology, EBSI seeks to streamline processes, reduce bureaucracy, and improve the overall user experience for individuals and organizations accessing public services.
The EBSI ecosystem operates by utilizing blockchain-based services infrastructure to enable the verification of credentials and data sharing among EU Member States. It ensures that information is securely stored and accessed across borders.
Nodes across Europe run blockchain-based services to authenticate transactions and validate the integrity of data exchanged within the network. This decentralized approach enhances the security and transparency of digital interactions within the EU.
Through the implementation of EBSI, users can benefit from a tamper-proof system that guarantees the authenticity and accuracy of information shared, leading to increased trust in digital exchanges.
The key features of EBSI include the issuance of verifiable credentials, enabling individuals to present digitally signed documents for verification. This enhances data integrity and reduces the risk of fraudulent activities.
Furthermore, EBSI facilitates the secure transfer of information across Member States, promoting interoperability and collaboration. It paves the way for advancements in technology by fostering innovation in digital services and solutions.
By utilizing blockchain technology, EBSI offers a reliable and efficient platform for storing and transmitting data, ensuring that public services are delivered with the highest standards of security and trust.
EBSI involves 29 EU Member States, along with Norway and Liechtenstein, in its collaborative efforts to establish a secure and efficient blockchain infrastructure for public services. These countries work together to enhance data sharing and verification processes.
The European Blockchain Partnership (EBP) oversees the implementation of EBSI, ensuring that all participating nations adhere to the shared standards and practices for blockchain-based services. This collaboration strengthens the integration of digital solutions across borders.
Through the cooperation of Member States and EBP, EBSI demonstrates the collective commitment to leveraging blockchain technology to drive digital transformation and enhance the delivery of public services throughout Europe.
The European Blockchain Services Infrastructure (EBSI) has made significant strides since its inception, marking a progressive journey towards harnessing blockchain technology for the public sector across Europe. Here’s a compiled overview of their history and progress:

Throughout its history, EBSI has evolved from a concept into a fully operational infrastructure. This demonstrates the transformative potential of blockchain technology in the public sector. This journey highlights not only technological advancements but also a collaborative effort across member states to embrace digital innovation for the betterment of European citizens and businesses.
European Blockchain Services Infrastructure (EBSI) has had a significant impact on the European Union by enabling trusted data sharing and facilitating the delivery of EU-wide cross-border public services using blockchain. By joining forces and running a blockchain-based services infrastructure, the EBSI nodes are able to create a network that operates in full respect of European values. This collaboration with the European Blockchain is a crucial step in harnessing the potential of blockchain-based services across the European Economic Area.
The EBSI use cases demonstrate the practical applications of blockchain technology in public administrations to streamline processes and improve efficiency. By utilizing the EBSI infrastructure, public services can be delivered securely and transparently, ensuring data integrity and privacy. EBSI nodes are spearheading cross-border, blockchain-enabled public services for the future.
EBSI has developed several frameworks to tackle business challenges using blockchain technology. The frameworks, categorized into Use Case families, target diverse sectors including education and SME finance and anti-counterfeiting. For example:
EBSI’s operational model is underpinned by its Core Technical Services, ensuring a uniform data flow across all use cases. The infrastructure’s decentralized network of nodes, governed by strict rules and standards, maintains the integrity and stability of the network. Node operators across Europe, approved by the European Blockchain Partnership, ensure a high level of security and availability. This contributes to a robust infrastructure without a single point of failure.
In summary, EBSI represents a significant step forward in the use of blockchain technology for public good. Setting a precedent for the future of digital services in Europe and potentially beyond. EBSI’s all-encompassing approach highlights blockchain’s transformative potential for public service delivery.

Welcome to the exciting world of blockchain! If you’ve ever wondered what this revolutionary technology…
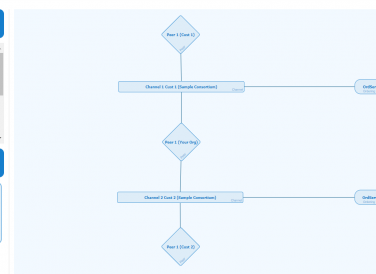
A few days ago the first demo video of AstraKode Blockchain was published on AstraKode’s YouTube channel. The video showcases…

Are you a small business owner who is wondering whether to adopt blockchain technology? Or,…