
Regulatory Compliance in Enterprise Blockchain
Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses, enabling secure and transparent transactions…

Smart contracts revolutionize the way we conduct financial transactions, but they still face security vulnerabilities. One such vulnerability known as reentrancy attack can jeopardize the security of smart contracts, causing significant financial loss. Understanding reentrancy attacks in Solidity is crucial for safeguarding smart contracts against this threat. We’ll examine reentrancy attacks, their methods, and prevention strategies to bolster smart contract security.
A reentrancy attack in the context of Ethereum smart contracts, particularly those written in Solidity, is a critical vulnerability where an attacker manipulates the contract’s withdrawal process. This exploit allows the attacker to repeatedly withdraw funds, akin to a thief continually drawing money from an account even after it should be empty. A reentrancy attack begins with a contract flaw, using an early external call to trigger a fund-draining loop.As famously demonstrated in the DAO hack, understanding and preventing reentrancy attacks are essential for secure smart contract development and operation.
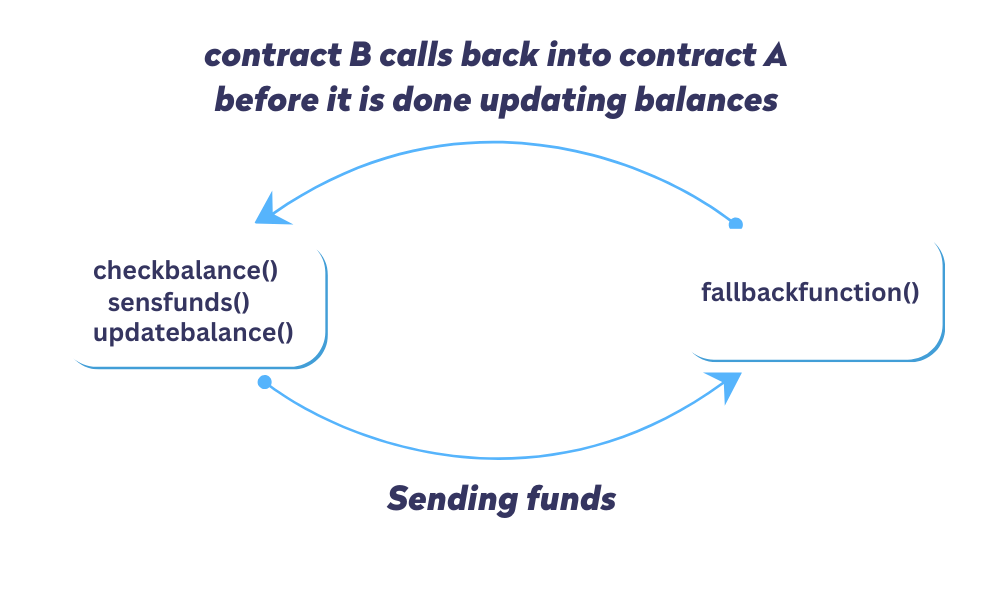
A reentrancy attack happens when the contract allows a function to be called again before the previous call finishes. This can lead to unexpected behavior and security vulnerabilities. To illustrate, imagine a function that transfers funds from one account to another. A malicious user could exploit a vulnerability in the function to repeatedly call it and drain the account before the transaction is complete. This demonstrates how reentrancy attacks can disrupt the expected flow of execution and compromise the security of a system.
There are several types of reentrancy attacks, including:
The DAO Attack (2016): This event is a landmark in the history of Ethereum and smart contracts. “The DAO” was an innovative idea, aiming to revolutionize how decentralized organizations operate. Tragically, it became the victim of a reentrancy attack, leading to a staggering loss of about $150 million in Ether. This attack not only drained the funds but also shook the trust in decentralized systems and was a wake-up call for the need for enhanced security in smart contracts.
Lendf.Me Hacks (April 2020): Both these platforms suffered significant financial losses due to a reentrancy attack, amounting to $25 million. These attacks showcased the vulnerabilities present even in well-known decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and emphasized the necessity for continuous security monitoring and upgrades in the DeFi ecosystem.
BurgerSwap Hack (May 2021): The $7.2 million loss due to a reentrancy exploit involving a fake token contract highlighted the sophisticated methods attackers use. It demonstrated that even seemingly secure smart contracts could be vulnerable to well-orchestrated exploits, stressing the importance of rigorous testing and validation of smart contracts, especially those dealing with token exchanges.
SURGEBNB Hack (August 2021): This attack, resulting in a $5 million loss, was particularly notable for its use of reentrancy in combination with price manipulation. It exemplified the multifaceted nature of smart contract attacks, where exploiters may use a mix of vulnerabilities to maximize their impact.
CREAM FINANCE Hack (August 2021): The $25 million loss in this incident showed how a single reentrancy vulnerability could be exploited to perform unauthorized actions like repeated borrowing, underlining the critical need for robust mechanisms like reentrancy guards in smart contract design.
In Solidity smart contracts, guarding against reentrancy vulnerabilities is crucial to prevent security breaches. Leveraging the inherent event-driven architecture of smart contracts, developers can employ events to create a tamper-proof record of all pivotal activities and state changes, ensuring a secure and verifiable transaction history on the blockchain ledger. This historical data is invaluable for tracking and substantiating the contract’s activity over time, serving as a crucial tool in detecting anomalies and reinforcing the robustness of security practices. It should work in tandem with the strategic state updates and meticulous management of external calls to form a holistic security framework.
To effectively mitigate these risks, focus on the following key prevention mechanisms:
Keeping up with the latest Solidity versions is crucial for enhancing smart contract security. Recent versions introduce improved syntax and compiler checks to mitigate vulnerabilities like reentrancy attacks, offering developers stronger safeguards against exploits. Developers must use reentrancy guards, update states before transfers, limit external calls, adopt pull payments, and conduct audits to lower vulnerability risks. Being informed about smart contract security developments is essential as the blockchain landscape evolves. Proactive security measures safeguard smart contracts on Ethereum, maintaining their integrity.

Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for businesses, enabling secure and transparent transactions…

In the vibrant landscape of blockchain technology, smart contracts have emerged as a game-changing innovation,…

In the dynamic world of blockchain technology, the concept of blockchain interoperability stands as a…